Names of cities in turkey – Embark on a journey through Turkey’s captivating cities, each boasting a unique blend of history, culture, and economic significance. From bustling metropolises to ancient ruins, Turkey’s urban landscape offers a rich tapestry of experiences.
Major cities in Turkey, such as Istanbul, Ankara, Izmir, Bursa, and Antalya, serve as vibrant hubs of commerce, culture, and tourism. Their strategic locations and rich histories have shaped their identities, making them fascinating destinations for travelers and residents alike.
List of Major Cities in Turkey
Turkey is a country with a rich history and culture, and its major cities reflect this diversity. From the bustling metropolis of Istanbul to the ancient ruins of Ephesus, Turkey’s cities offer a fascinating glimpse into the country’s past and present.
The following is a list of the major cities in Turkey, organized in descending order of population:
Istanbul
- Population: 15,840,900
- Location: Marmara Region, on the shores of the Bosporus Strait
- Historical and cultural significance: Istanbul is Turkey’s largest city and its former capital. It is a major cultural and economic center, and home to many historical and religious landmarks, including the Hagia Sophia, the Blue Mosque, and the Topkapi Palace.
Ankara
- Population: 5,747,325
- Location: Central Anatolia Region, in the heart of Turkey
- Historical and cultural significance: Ankara is Turkey’s capital city and the seat of government. It is also a major cultural and economic center, and home to many museums, theaters, and universities.
Izmir
- Population: 4,425,789
- Location: Aegean Region, on the coast of the Aegean Sea
- Historical and cultural significance: Izmir is Turkey’s third-largest city and a major port city. It is a major cultural and economic center, and home to many historical and religious landmarks, including the Ephesus ruins, the House of the Virgin Mary, and the Izmir Archaeological Museum.
Bursa
- Population: 3,147,810
- Location: Marmara Region, in the northwest of Turkey
- Historical and cultural significance: Bursa was the first capital of the Ottoman Empire and is home to many historical and religious landmarks, including the Grand Mosque of Bursa, the Green Mosque, and the Tophane Clock Tower.
Antalya
- Population: 2,607,320
- Location: Mediterranean Region, on the coast of the Mediterranean Sea
- Historical and cultural significance: Antalya is a major tourist destination and is home to many historical and religious landmarks, including the Hadrian’s Gate, the Perge ruins, and the Aspendos Amphitheater.
Konya
- Population: 2,277,210
- Location: Central Anatolia Region, in the south of Turkey
- Historical and cultural significance: Konya was the capital of the Seljuk Empire and is home to many historical and religious landmarks, including the Mevlana Museum, the Alaeddin Mosque, and the Sille ruins.
Adana
- Population: 2,263,373
- Location: Mediterranean Region, in the south of Turkey
- Historical and cultural significance: Adana is a major industrial and agricultural center and is home to many historical and religious landmarks, including the Great Mosque of Adana, the Ramazanoğlu Mansion, and the Adana Archaeological Museum.
Gaziantep
- Population: 2,134,436
- Location: Southeastern Anatolia Region, in the southeast of Turkey
- Historical and cultural significance: Gaziantep is a major industrial and agricultural center and is home to many historical and religious landmarks, including the Gaziantep Castle, the Zeugma Mosaic Museum, and the Bayazhan Mosque.
Kayseri
- Population: 1,437,753
- Location: Central Anatolia Region, in the center of Turkey
- Historical and cultural significance: Kayseri was a major center of the Hittite Empire and is home to many historical and religious landmarks, including the Kayseri Castle, the Hunat Hatun Mosque, and the Kayseri Archaeological Museum.
Trabzon
- Population: 810,101
- Location: Black Sea Region, on the coast of the Black Sea
- Historical and cultural significance: Trabzon was the capital of the Byzantine Empire and is home to many historical and religious landmarks, including the Hagia Sophia of Trabzon, the Sumela Monastery, and the Atatürk Pavilion.
Geographic Distribution of Cities in Turkey
The geographic distribution of cities in Turkey is influenced by several factors, including proximity to major waterways, coastal areas, and mountain ranges. Turkey’s cities are primarily concentrated in the western and northwestern regions, with a significant number of urban centers located along the coastlines of the Aegean and Mediterranean Seas.
The country’s largest city, Istanbul, is situated at the confluence of the Bosphorus Strait and the Sea of Marmara, making it a strategic hub for trade and commerce.
Regions with Higher Concentrations of Cities
The regions with the highest concentrations of cities in Turkey are:
- Marmara Region:This region, which includes Istanbul, is the most urbanized in Turkey, with over 20 million inhabitants. The region’s proximity to the Bosphorus Strait and the Sea of Marmara has contributed to its economic and cultural significance.
- Aegean Region:The Aegean Region, located along the Aegean Sea coast, is home to several major cities, including Izmir, Bursa, and Antalya. The region’s mild climate and fertile soil have made it a center for agriculture and tourism.
- Mediterranean Region:The Mediterranean Region, which borders the Mediterranean Sea, is known for its warm climate and beautiful beaches. Major cities in this region include Adana, Mersin, and Antalya.
The distribution of cities in Turkey is also influenced by the country’s mountainous terrain. The Taurus Mountains, which run along the southern coast, and the Pontic Mountains, which extend along the northern coast, have limited the development of urban centers in some areas.
However, these mountains have also created natural barriers that have helped to preserve the country’s diverse cultural and linguistic heritage.
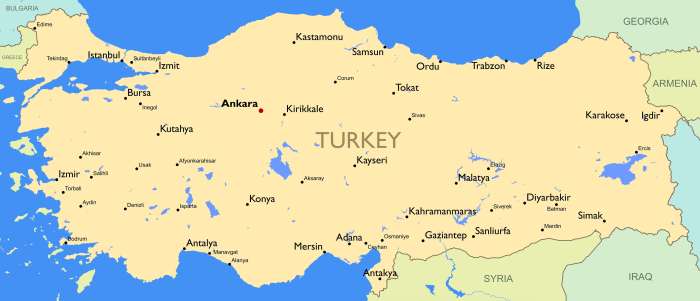
The following map illustrates the geographic distribution of cities in Turkey:
[Image of a map of Turkey showing the distribution of cities]
Economic Importance of Turkish Cities
Major cities in Turkey are the driving force behind the country’s economic growth and development. They contribute significantly to the national GDP, acting as industrial hubs, financial centers, and tourism destinations.
Industrial Hubs
Turkey’s major cities are home to a wide range of industries, including textiles, automotive, food processing, and electronics. These industries generate a substantial portion of the country’s exports and provide employment to millions of people. For example, Istanbul, the largest city in Turkey, is a major center for textiles and apparel manufacturing.
Financial Centers
Istanbul is also Turkey’s financial hub, hosting the headquarters of major banks and financial institutions. The city’s financial sector plays a crucial role in mobilizing capital and facilitating investment throughout the country.
Tourism Destinations
Turkey’s major cities are popular tourist destinations, attracting millions of visitors each year. Tourism is a major source of foreign exchange and employment for the country. Istanbul, Antalya, and Cappadocia are among the most visited cities, renowned for their historical sites, cultural attractions, and natural beauty.
Historical Significance of Turkish Cities
Turkey, a country spanning two continents, is home to a rich and diverse history. Throughout centuries, its cities have played pivotal roles in shaping the course of human civilization. From the ancient ruins of Troy to the bustling metropolis of Istanbul, Turkish cities have witnessed the rise and fall of empires, the clash of cultures, and the birth of groundbreaking ideas.
Ankara: The Capital of Modern Turkey
Ankara, the modern capital of Turkey, has a rich history dating back to the Hittites. It was conquered by the Romans, Byzantines, and Seljuks before becoming the capital of the Ottoman Empire in the 14th century. After the fall of the empire, Ankara emerged as the center of the Turkish national movement and became the capital of the newly founded Turkish Republic in 1923.
Istanbul: The Crossroads of Civilizations
Istanbul, once known as Constantinople, is one of the most historically significant cities in the world. Founded by the Greeks in the 7th century BC, it served as the capital of the Byzantine Empire for over a thousand years. In 1453, the city was conquered by the Ottoman Turks, who transformed it into the capital of their vast empire.
Istanbul remained the center of the Ottoman Empire until its collapse in 1922. Today, Istanbul is a vibrant metropolis and a cultural melting pot, home to people from all over the world.
Ephesus: A Thriving Ancient City
Ephesus, located on the Aegean coast of Turkey, was one of the most important cities in the ancient world. Founded by the Greeks in the 11th century BC, it became a major center of trade and culture. Ephesus was home to the Temple of Artemis, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World.
The city was later conquered by the Romans and became the capital of the Roman province of Asia. Ephesus is now a UNESCO World Heritage Site and one of the most popular tourist destinations in Turkey.
Troy: The Legendary City of Homer
Troy, located in northwestern Turkey, is one of the most famous cities in history. It is best known for its role in the Trojan War, which was immortalized in Homer’s epic poem the Iliad. The city was besieged by the Greeks for ten years before it was finally captured and destroyed.
Troy has been the subject of archaeological excavations for over a century, and its ruins are now a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Cultural Diversity of Turkish Cities
Turkey’s major cities are renowned for their cultural diversity, reflecting the country’s rich history and strategic location at the crossroads of Europe and Asia.
This diversity is evident in the cities’ ethnic, linguistic, and religious makeup, with various communities contributing to the vibrant cultural fabric of these urban centers.
Ethnic Diversity
- Istanbul:Home to a diverse mix of Turkish, Kurdish, Armenian, Greek, and Jewish communities.
- Ankara:A melting pot of Turkish, Kurdish, and Circassian cultures.
- Izmir:Known for its significant Greek and Jewish populations, as well as a large Armenian community.
Linguistic Diversity, Names of cities in turkey
- Turkish:The official language spoken throughout the country.
- Kurdish:Widely spoken in southeastern Turkey, with distinct dialects spoken by different Kurdish communities.
- Arabic:Spoken by significant Arab communities in cities like Istanbul and Gaziantep.
- Greek:Still spoken by small Greek communities in Istanbul and Izmir.
- Armenian:Spoken by Armenian communities in Istanbul, Ankara, and Diyarbakır.
Religious Diversity
- Islam:The dominant religion in Turkey, with the majority of the population identifying as Sunni Muslims.
- Christianity:Orthodox Christianity is practiced by the Greek Orthodox Church and the Armenian Apostolic Church, while Catholicism is present in Istanbul and Izmir.
- Judaism:Istanbul has a historic Jewish community, with synagogues and cultural institutions.
Cultural Events and Landmarks
The cultural diversity of Turkish cities is reflected in numerous cultural events, festivals, and landmarks:
- Istanbul International Film Festival:A prestigious film festival showcasing global cinema.
- Ephesus Festival:A summer festival held in the ancient city of Ephesus, featuring performances and exhibitions.
- Hagia Sophia:A historic Byzantine church and later a mosque, now a museum, symbolizing the city’s religious and cultural heritage.
- Topkapi Palace:A former Ottoman palace, now a museum, showcasing the grandeur and history of the Ottoman Empire.
Architectural Heritage of Turkish Cities
Turkey’s cities are a treasure trove of architectural wonders, reflecting the country’s rich history and cultural diversity. From ancient ruins to modern masterpieces, the architectural heritage of Turkey’s major cities showcases a fascinating blend of styles and influences.
One of the most iconic landmarks in Turkey is the Hagia Sophia in Istanbul. Originally built as a Byzantine basilica in the 6th century, it was later converted into a mosque and then a museum. The Hagia Sophia’s massive dome and intricate mosaics are a testament to the architectural prowess of the Byzantine Empire.
Another architectural marvel in Istanbul is the Blue Mosque. Built in the 17th century, the Blue Mosque is famous for its six minarets and its interior, which is decorated with exquisite blue tiles. The mosque’s grandeur and beauty are a reflection of the Ottoman Empire’s power and wealth.
In Ankara, the capital of Turkey, the Kocatepe Mosque is a modern architectural masterpiece. Completed in 1987, the mosque is one of the largest in the world and its design incorporates elements of traditional Turkish architecture with modern materials and techniques.
The ancient city of Ephesus, located on the Aegean coast, is home to some of the best-preserved Roman ruins in the world. The city’s amphitheater, library, and agora are just a few of the many architectural wonders that can be explored in Ephesus.
The architectural heritage of Turkey’s cities is a testament to the country’s rich history and cultural diversity. From ancient ruins to modern masterpieces, Turkey’s cities offer a fascinating glimpse into the past and present of this vibrant country.
Infrastructure and Transportation in Turkish Cities
Turkey’s major cities have a well-developed infrastructure and transportation system that supports their economic growth and connectivity. Road networks connect cities and towns, facilitating trade and travel. Public transportation systems, including buses, trams, and metro lines, provide convenient and affordable options for urban mobility.
Major cities also have international airports, serving as gateways to Turkey and beyond.
Challenges and Opportunities in Urban Planning and Infrastructure Development
Rapid urbanization and population growth in Turkish cities pose challenges to infrastructure development. Traffic congestion, air pollution, and access to affordable housing are common issues. Urban planning strategies focus on sustainable development, promoting public transportation, walkability, and green spaces to enhance urban livability.
Road Networks
Turkey’s road network is extensive, connecting all major cities and regions. Highways and motorways facilitate long-distance travel, while urban roads provide access within cities. However, traffic congestion is a challenge in metropolitan areas, leading to infrastructure improvements and traffic management initiatives.
Public Transportation
Public transportation plays a vital role in urban mobility in Turkey. Buses are the most common form, operating in all major cities. Tram and metro lines provide efficient and reliable transportation in densely populated areas. Istanbul’s metro system is one of the largest in Europe, serving millions of passengers daily.
Airports
Turkey has several international airports, including Istanbul Airport, which is a major hub for both domestic and international travel. Other major airports include Ankara Esenboğa Airport, İzmir Adnan Menderes Airport, and Antalya Airport. These airports facilitate trade, tourism, and connectivity with the rest of the world.
Case Study: Istanbul’s Transportation System
Istanbul’s transportation system is a complex and comprehensive network that caters to the needs of its vast population. The city has an extensive bus network, supplemented by a metro system, tram lines, and ferries. The Istanbulkart, a contactless payment system, provides seamless integration between different modes of transportation.
Statistics
- Turkey has over 60,000 kilometers of highways and motorways.
- Istanbul’s metro system has over 100 stations and carries over 2 million passengers daily.
- Istanbul Airport is one of the busiest airports in Europe, handling over 100 million passengers annually.
Tourism and Hospitality in Turkish Cities
The tourism industry is a vital part of the Turkish economy, contributing significantly to the country’s GDP and employment. Major cities in Turkey, such as Istanbul, Ankara, and Antalya, are popular tourist destinations, attracting millions of visitors each year. These cities offer a diverse range of attractions, including historical landmarks, cultural heritage sites, and natural wonders.
One of the most popular tourist attractions in Turkey is the Hagia Sophia, a former Byzantine church that was later converted into a mosque and is now a museum. Other popular attractions include the Blue Mosque, the Topkapi Palace, and the Grand Bazaar, all located in Istanbul.
In Ankara, the capital of Turkey, visitors can explore the Museum of Anatolian Civilizations, which houses a vast collection of artifacts from Turkey’s rich history. Antalya, on the Mediterranean coast, is known for its beautiful beaches, stunning coastline, and ancient ruins.
Economic Impact of Tourism
The tourism industry has a significant economic impact on Turkey. In 2019, the sector contributed over 12% to the country’s GDP and employed over 2 million people. Tourism revenue is a major source of foreign exchange for Turkey, helping to support the country’s economy and create jobs.
Hospitality Sector
The hospitality sector in Turkey plays a vital role in supporting the tourism industry. The country has a wide range of hotels, resorts, and other accommodation options to cater to the needs of visitors. The hospitality sector also provides employment for many people in Turkey, including hotel staff, tour guides, and restaurant workers.
Tourist Arrivals
Turkey has seen a steady increase in tourist arrivals in recent years. In 2019, the country welcomed over 51 million visitors, a 10% increase from the previous year. The majority of tourists come from Europe, with Germany, Russia, and the United Kingdom being the top source markets.
However, Turkey is also becoming increasingly popular with tourists from other regions, such as Asia and the Middle East.
Hotel Occupancy Rates
Hotel occupancy rates in Turkey have been relatively high in recent years, averaging over 70% in major cities. This indicates that there is strong demand for hotel accommodation in Turkey, particularly during the peak tourist season.
Visitor Spending
Visitors to Turkey spend a significant amount of money on accommodation, food, beverages, and other expenses. In 2019, tourists spent an estimated $34 billion in Turkey, a 12% increase from the previous year. This spending helps to support the local economy and create jobs.
Education and Healthcare in Turkish Cities: Names Of Cities In Turkey
Turkish cities offer a wide range of educational and healthcare services, with varying quality and accessibility. Major cities like Istanbul, Ankara, and Izmir boast renowned universities, hospitals, and specialized medical centers.
Educational Quality and Accessibility
Literacy rates in Turkey have steadily increased over the past decades, reaching 99% in major cities. The country has a comprehensive education system that includes primary, secondary, and higher education institutions. Public schools provide free education, while private schools offer alternative curricula and often higher academic standards.Universities
in major cities like Istanbul, Ankara, and Izmir are highly ranked internationally, offering a diverse range of programs in various disciplines. However, access to higher education can be competitive, with entrance exams determining admission.
Healthcare Quality and Accessibility
Turkey’s healthcare system is a mix of public and private providers. Public hospitals offer affordable healthcare, while private hospitals provide more advanced facilities and services. The quality of healthcare varies, with major cities having better-equipped hospitals and specialized medical centers.Access
Turkey boasts an array of captivating cities, each with its unique charm. From the bustling streets of Istanbul to the serene shores of Antalya, the country’s urban landscapes offer a rich tapestry of history and culture. While exploring these cities, travelers seeking a luxurious and indulgent vacation experience may consider exploring five star all inclusive europe options in Turkey.
These resorts provide unparalleled amenities, exceptional service, and exclusive access to some of the country’s most stunning beaches and historical sites.
to healthcare can be influenced by factors such as income, insurance coverage, and geographic location. However, Turkey’s universal health insurance system ensures that all citizens have access to basic healthcare services.
Areas for Improvement
While Turkish cities offer a generally high standard of education and healthcare, there are areas for improvement.* Education:Improving equity in access to quality education, particularly for disadvantaged communities.
Healthcare
Reducing waiting times for specialized medical services, expanding access to mental health care, and addressing disparities in healthcare outcomes between different regions.By investing in these areas, Turkey can further enhance the quality of life and well-being of its urban population.
Future Trends and Challenges for Turkish Cities
As Turkey’s urban landscape continues to evolve, its major cities face a range of future trends and challenges that will shape their development trajectories. These include rapid urbanization, climate change impacts, and the transformative effects of technological advancements.
To navigate these challenges and ensure sustainable urban development, Turkish cities will need to adopt innovative strategies that promote economic growth, social equity, and environmental resilience.
Urbanization
Turkey’s urban population is projected to continue growing in the coming decades, putting pressure on infrastructure, housing, and public services. Cities will need to invest in compact, mixed-use development, public transportation, and affordable housing to accommodate this growth while minimizing its negative impacts.
Climate Change
Climate change is expected to bring more extreme weather events, sea-level rise, and water scarcity to Turkish cities. Cities will need to develop adaptation and mitigation strategies to reduce their vulnerability to these impacts, such as investing in green infrastructure, improving water management systems, and promoting renewable energy.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements, such as artificial intelligence, automation, and the internet of things, are transforming urban life. Cities will need to embrace these technologies to improve efficiency, enhance public services, and create new economic opportunities while addressing potential challenges related to job displacement and privacy concerns.
Wrap-Up
Exploring the names of cities in Turkey is akin to delving into a treasure trove of history, culture, and modern-day vitality. Each city holds a distinct charm, inviting visitors to immerse themselves in its unique offerings. From the grandeur of Istanbul to the vibrant streets of Izmir, Turkey’s urban tapestry is a testament to the country’s rich heritage and promising future.
FAQ
What are the largest cities in Turkey?
Istanbul, Ankara, Izmir, Bursa, and Antalya are the five largest cities in Turkey.
What is the capital of Turkey?
Ankara is the capital city of Turkey.
What is the most popular tourist destination in Turkey?
Istanbul is the most popular tourist destination in Turkey, known for its iconic landmarks, rich history, and vibrant culture.


